Distal Medial Process of the Humerus Joins the Ulna
Distal medial process of the humerus. Bones that articulate with the clavicle.

Humerus Radius Ulna Anatomy Bones Anatomy Medical Anatomy
Distal medial process of the humerus.

. The distal meaning furthest from the body aspect of the humerus that forms the elbow is called the trochlea which literally means pulleyThe distal medial aspect of the humerus in the region. Distally the humerus joins medially with the ulna and laterally with the radius at the elbow joint. Distalend feature medial styloid processfor wrist ligaments OpenStax Fig 86 Ulna and Radius.
Compared to the radius the dimensions of the ulna are reversed because it has a. Anterior depression superior to the trochlea that receives part of the ulna when the forearm is flexed. Distal medial process of the humerus.
Bones of the wrist. Femur tibia fibula patella tarsals. The radius is shorter than the ulna and has a small proximal end that articulates with the humerus and a broad distal end that articulates with the carpal bones at the wrist.
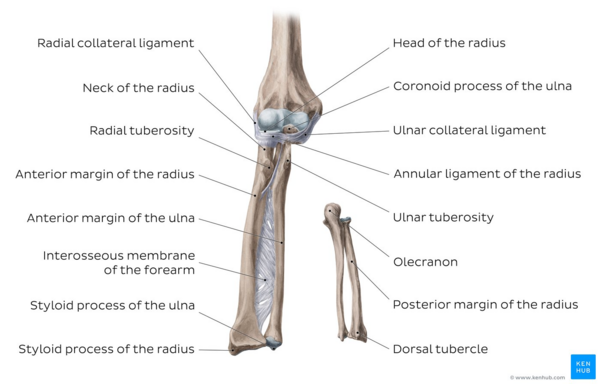
The humeroradial joint is formed by the rounded capitulum of the humerus and the concave superior surface of the radial head. Orientation and general presentation Figs 101 102 The ulna 1 is located on the medial aspect of the forearm. The ulna is located on the right side or medial side of the forearm.
Bones of the wrist. Proximalend features 1 Trochlearsemilunar notch articulates with trochlea of humerus 2 Olecranon process 3 Coronoid process 4 Radial notch b. Medial bone of the forearm in anatomical position little finger side.
Medial bone of the forearm in anatomical position. Anterior depression superior to the trochlea that receives part of the ulna when the forearm is flexed. Receives part of the ulna when the forearm is flexed.
It can be continuous with the ligament of Struthers beneath which the median nerve and brachial artery pass. The larger process is the olecranon process. Bones that articulate.
The humeroulnar joint is formed by the pulley-shaped trochlea of the humerus and the trochlear notch of the ulna. Medial bone of the forearm in. The ulna is located on the right side or medial side of the forearm.
FIGURE 171 The distal-most part of the lateral column is the capitellum and the distal-most part of the medial column is the nonarticular medial epicondyle. The trochlear notch of the ulna is a C-shaped surface that fits on the trochlea. The intramedullary canal of the humerus ends 2 to 3 cm above the olecranon fossa.
It articulates with the humerus 2 proximally the wrist complex 3 distally and the radius 4 laterally. Forearm bone involved in formation of elbow joint. The supracondylar process is a variant that is found 5 cm above the medial epicondyle and can be 2 to 22 mm in length.
The ulnohumeral joint is a constrained joint with the proximal ulna olecranon rotating on the fixed axis of the distal humerus trochlea. The trochlear notch of the ulna is a C-shaped surface that fits on the trochlea. Key facts about the humerus.
Receives part of the ulna when the forearm is flexed. Distal medial process of the humerus. The nature of the elbow joint enables the movements that are limited to the arm and forearm and cannot be performed within the other parts of the body such as supination and pronation.
This structure is often considered a vestigial structure as a supracondylar canal or foramen can be found as a normal structure in many more primitive mammals such as. Rounded knob on the humerus that articulates with the radius. On the lateral edge of the coronoid process is the small radial notch that forms the proximal radioulnar joint with the radius and permits the radius to rotate.
The proximal epiphysis of the ulna bone shows a joint cavity the semilunar notch or greater sigmoid cavity 5 which can be divided into two. The ulna articulates at its proximal end with the trochlea of the humerus. Humerus radius ulna carpals.
The supracondylar spur is typically located on the anteromedial humeral cortex 5 cm proximal to and pointing towards the medial epicondyle of the humerus 3. In the anatomical position the radius is found in the lateral forearm while the ulna is found in the medial forearm. Superior to the trochlea.
Rounded knob on the humerus that articulates with the radius. Head of the ulna edit edit source The lateral distal end of the ulna is the head of the ulna. On the lateral side of the coronoid process is the radial notch where the head of the radius sits.
Superior to the trochlea. The ulna articulates at its proximal end with the trochlea of the humerus. Also the humerus has distal articulations with the radius and ulna at the elbow joint.
Medial bone of the forearm in anatomical position. 77 rows Distal medial process of the humerus. Bones that articulate with the clavicle.
It is composed of the trochlea capitellum and medial and lateral epicondyles. The coronoid process also forms the lower part of the semi-lunar notch. Medial bone of the forearm in anatomical position.
The proximal and distal ends of the humerus are cancellous. Distal medial process of the humerus. The flexionextension arc in normal individuals ranges from 0 degrees full extension to approximately 135 degrees full flexion.
The trochlear axis is 3 to 8 degrees internally rotated. Forearm bone most involved in formation of the elbow joint. The more medial of these areas is the trochlea a spindle- or pulley-shaped region trochlea pulley which articulates with the ulna bone.
It is received into the coronoid fossa of the humerus in elbow flexion. The distal end of the humerus has two articulation areas which join the ulna and radius bones of the forearm to form the elbow joint. The ulna and radius are the two bones in the forearm.
The trochlea is the medial-most part of the articular segment and is. Forearm bone involved in formation of elbow joint. The trochlear notch is made up of two processes.
The distal lip of the trochlear notch protrudes anteriorly to form the coronoid process that helps to lock the ulna in place with the humerus at the elbow and fits into the coronoid fossa of the humerus. Medial bone of the forearm in anatomical position.


No comments for "Distal Medial Process of the Humerus Joins the Ulna"
Post a Comment